-
Telephone:400-000-0000Telephone:400-000-0000
-
wechat:abcdefg
-
Email:sales@ahxsgd.com

1. Brief introduction of cavity ring down spectroscopy (CRDS) technology
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (Cavity Ring-Down Spectroscopy) is a highly sensitive absorption spectrum detection technique based on the absorptivity of cyclic light in the optical cavity. The technology can be applied to physics, atmosphere, environment and analytical chemistry, as well as combustion science, physics, medical diagnosis and biology.
Optical resonator is the core component of optical cavity decay spectroscopy (CRDS) detection technology. it mainly uses two mirrors with ultra-high reflectivity (≥ 99.99%) to form the ring-down optical path of laser reciprocating reflection, which can not only greatly improve the number of reflections in the optical cavity, but also form a very long absorption optical path, so as to achieve ultra-high precision gas absorption spectrum monitoring function.
Second, the technical principle of cavity ring down spectroscopy (CRDS).
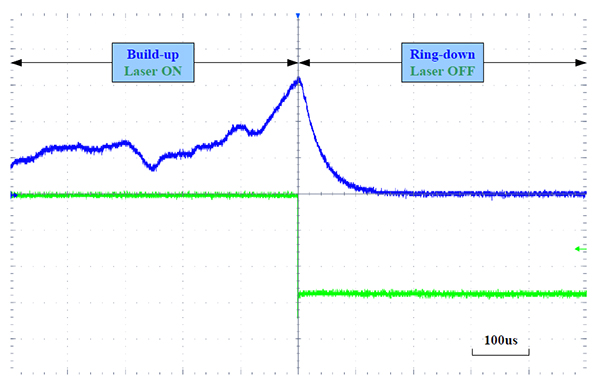
The optical cavity decay spectroscopy is different from other direct absorption spectroscopy in that the latter calculates the gas concentration by measuring the energy change of the light before and after passing through the sample gas. the optical cavity decay is based on the decay time of the light in the sample cavity to calculate the energy decay rate and calculate the concentration of the gas in the cavity. The decay time of light is called cavity decay time, which is inversely proportional to all the losses in the cavity. Therefore, by measuring the light attenuation time (rather than the total intensity) in the sample cavity, the absorptivity can be determined and the loss on the absolute scale can be provided directly. In the case of no gas in the sample cavity, the loss is only determined by the reflectivity of the cavity reflector, and the injection climate in the cavity will lead to greater light loss, thus shrinking the decay time.
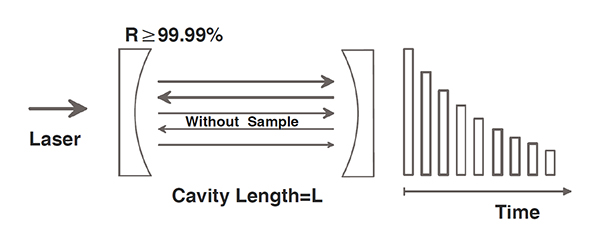
Schematic diagram of energy attenuation of optical cavity ring-down spectroscopy (1. Without sample)
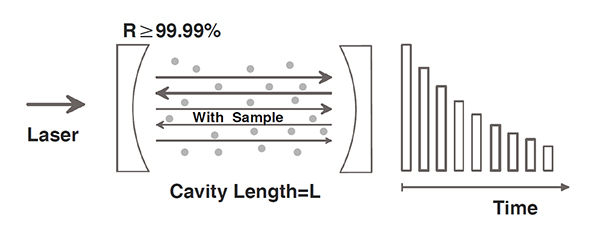
Schematic diagram of energy attenuation of optical cavity ring down spectroscopy (2. With sample)
In the case of a cavity without sample gas, the time constant T0 of light attenuation depends on the reflection loss of the mirror, which can be expressed as follows:
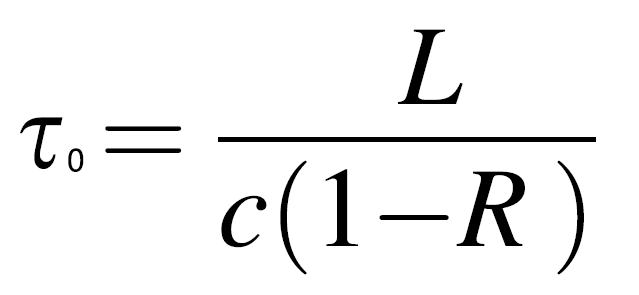
Where C is the speed of light in vacuum, L is the length of the optical cavity, and R is the reflectivity of the mirror.
When the sample gas is filled in the cavity, the decay time of 1max e of this exponential decay light intensity is called attenuation time T1, which can be expressed as:
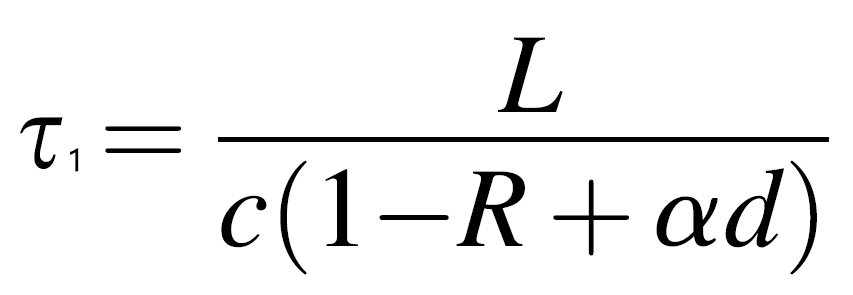
Where d is the length of the sample and an is the absorption coefficient of the sample.
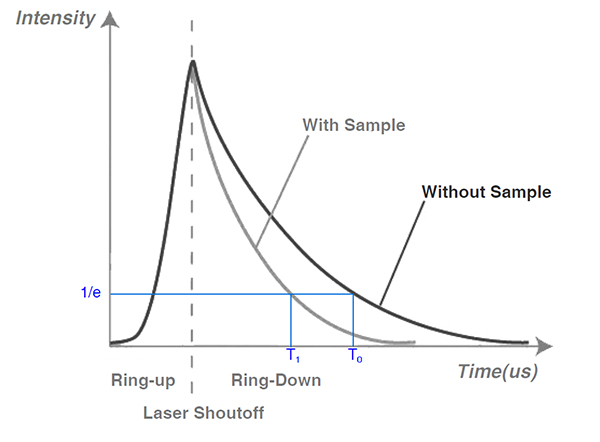
The absorption coefficient a can be calculated by obtaining the data of T0 and T1, and the concentration of trace gas can be obtained by combining Bill Lambert's law.
The effective optical path of the gas cell used in optical cavity ring-down spectroscopy is usually thousands of meters long, which is different from Herriot cell and White cell. Before the laser enters the special optical cavity for optical cavity ring-down spectrum, it is necessary to match the laser mode with the optical cavity mode. Bill Lambert's CRDS laser cavity decay gas cell integrates a cavity mode matching optical system and a photodetector without the need for users to participate in the adjustment of the internal opto-mechanical structure. The butterfly-shaped distributed feedback (DFB) laser is supported as the light source. As long as the laser is connected to the product through the optical fiber interface and the electrical connection configuration is completed, the high-quality cavity ring-down signal can be obtained, which brings great convenience to the user.

Optical cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) is mainly used in the fields of environmental monitoring, molecular spectroscopy, atmospheric sensing, breath diagnosis, plasma diagnosis, kinetic research, aerosol extinction and absorption monitoring.
The above is a very simple preliminary introduction of optical cavity ring down spectroscopy (CRDS) technology, and many problems will be involved in its specific application, such as the structure of the optical path, the influence of the application environment, the processing of the detection signal, the analysis and processing of the spectrum, and so on. Each step is a relatively complicated technology, if you need to know more, please contact us.

