-
Telephone:400-000-0000Telephone:400-000-0000
-
wechat:abcdefg
-
Email:sales@ahxsgd.com

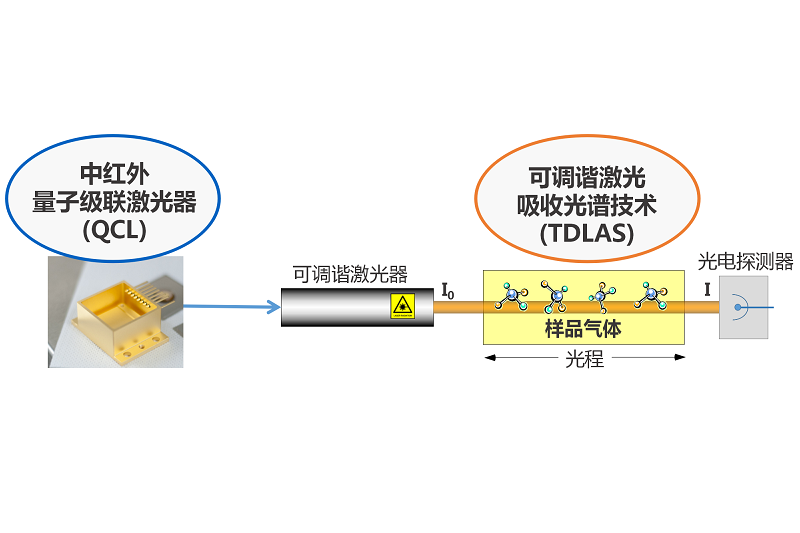
Born in 1994 at the famous Bell Laboratory in the United States, the Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) is a new type of monopole semiconductor laser based on the principle of inter-band transition of electrons in semiconductor quantum wells and phonon-assisted resonant tunneling. It works in a traditional near-infrared diode laser. The working principle is essentially different, and its lasing wavelength can cover most of the mid-to-infrared spectral regions.
As quantum cascade laser technology matures, it has begun to be used more in scientific and engineering research. Due to its significant advantages, it has been rapidly promoted in the field of gas detection. Infrared spectral gas detection technology based on quantum cascade lasers has the advantages of high sensitivity and fast detection speed, especially its significant advantages in high-precision spectral detection, making it a hot spot in research and application.
It has broad prospects in application directions such as environmental pollution monitoring, high-precision monitoring of industrial processes, and detection of trace drugs and explosives. The combination of semiconductor QCL and TDLAS optical sensing technology can effectively detect the basic energy levels of molecules with wavelengths in the mid-infrared (wavelengths of 3um to 20um).